CHAPTER 9. OBJECTIVE 6: WEATHER-RELATED DECISION SUPPORT TECHNOLOGIES ARE INTEGRATED INTO TRAFFIC OPERATIONS AND MAINTENANCE PROCEDURESThe implementation of weather-related decision support technologies help State departments of transportation (DOT) deploy a more sophisticated approach to traffic operations and maintenance by factoring in the impact of adverse weather conditions. The performance measures (PM) under Objective 6 examine the various ways in which weather-related decision support technologies can be integrated into agency decision-making. PM #19: Number of agencies adopting maintenance decision support systems technologies and methodsEvaluations of maintenance decision support systems (MDSS) technologies and methods have shown significant benefits to State and local agencies including cost savings on materials and labor, and improved highway operations. Adoption of MDSS indicates that more agencies are moving towards advanced approaches to managing their maintenance decisions and operations during winter seasons. Since 2004, the Road Weather Management Program (RWMP) has advocated the adoption of MDSS technology, and this performance measure captures the number of State DOTs that have adopted MDSS technologies and to what extent. The results of the 2015 State DOT survey are compared with the results from the 2012 update in Figure 18 below. 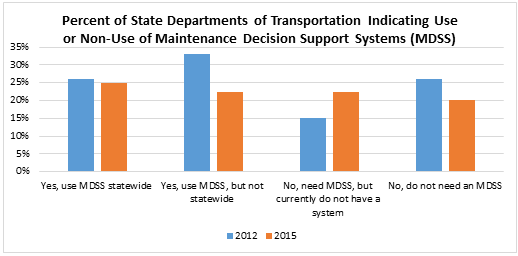 Figure 18. Graph. Percent of State Departments of Transportation Indicating Use or Non-Use of Maintenance Decision Support Systems. The percentage of State DOTs with statewide MDSS deployment has remained constant, and partial MDSS use has decreased. Perhaps more significant is that the number of State DOTs expressing a need for MDSS increased, with a corresponding decrease in those agencies reporting no need for a system. PM #20: Number of agencies using other weather-related decision-support toolsWeather-related decision-support tools help agencies increase the effectiveness of their road weather management practices. The array of tools available assists agencies and their staff in making more informed decisions. This performance measure captures the number of State DOTs employing operations decision support tools – other than MDSS – to respond to a range of weather conditions, beyond winter maintenance activities (i.e., snow and ice control), as captured in Figure 19. 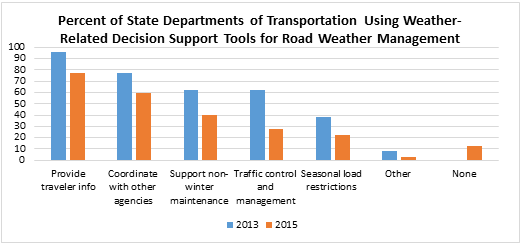 Figure 19. Graph. Percent of State Departments of Transportation Using Weather-Related Decision Support Tools for Road Weather Management. Compared to 2013, the State DOTs respondents indicate an overall decrease in the use of weather-related decision support tools for road weather management, and a few states (12.5 percent) reported not using any tools. Despite the decrease in the use of decision support tools, the relative uses of the tools remain unchanged. Providing traveler information remains the most used tool, followed by coordination with other agencies, support of non-winter maintenance, traffic control and management, seasonal load restrictions and other. PM #21: Number of agencies reporting use of appropriate analysis tools to factor weather impacts and strategiesTraditionally, traffic modeling and analysis tools have assumed perfect weather, making it difficult for an agency to adequately consider weather impacts and strategies. Increasingly, weather-responsive microscopic and mesoscopic traffic analysis and modeling tools are available to help agencies conduct more realistic traffic analyses. This measure shows the number of agencies employing analysis tools that consider adverse weather impacts and strategies. 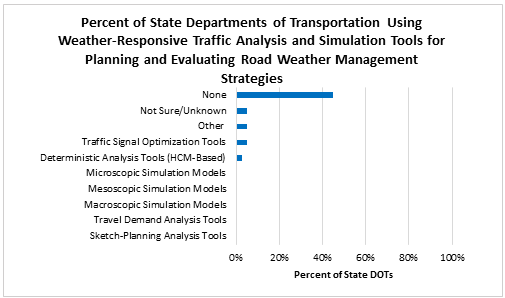 Figure 20. Graph. Percent of State Departments of Transportation Using Weather-Responsive Traffic Analysis and Simulation Tools for Planning and Evaluating Road Weather Management Strategies. Results from the survey, shown in Figure 20, indicate that 50 percent of the respondents either did not use or were not aware of whether their agency used weather-responsive tools and models. This indicates greater use of these types of tools and models from the previous update, in which 83 percent of State DOTs responding indicated that their agency did not use weather-responsive tools and models.(35) Of the types of tools and models identified, Traffic Signal Optimization Tools that factor in weather conditions are the most commonly used (5 percent), followed by Deterministic Analysis Tools (Highway Capacity Manual [HCM]-based). None of the State DOTs indicated using Microscopic Simulation Tools, Mesoscopic Simulation Tools, Macroscopic Simulation Tools, Travel Demand Analysis Tools, or Sketch Planning Analysis Tools. SummaryThe performance measures for this objective represent an opportunity for significant improvement. RWMP efforts in this area should focus on encouraging the use of MDSS and more sophisticated weather-responsive tools and models (analysis and modeling.), and increasing the availability and use of decision support tools other than MDSS. 35 Further comparison to data from the previous survey is not possible, as the measure was defined differently in this update. [ Return to note 35. ] |
|
United States Department of Transportation - Federal Highway Administration |
||