| Skip
to content |
|
Urban Freight Case Studies - New York CityGeographic DescriptionNew York City consists of five boroughs: The Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island. Manhattan, which has a land area of only 22.96 square miles and a population of 1.63 million, has the largest central business district in the United States.2 As shown in Figure 1, roadway connections to this borough include three bridges and one tunnel to/from Brooklyn, two tunnels and one bridge to/from New Jersey, three bridges to/from the Bronx and two bridges and one tunnel to/from Queens. Vehicles entering or leaving these access points experience heavy traffic on bridges and tunnels. Figure 1: Manhattan Bridge and Tunnel Crossings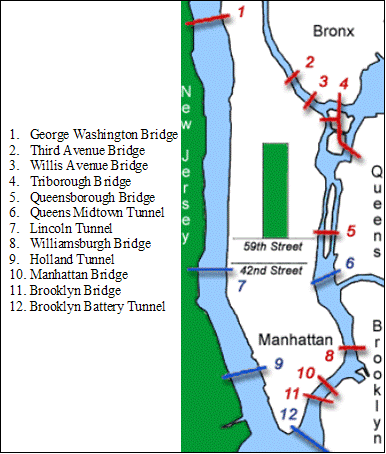
Source: NY.com, NYC Bridge and Tunnel Crossings, available at http://www.ny.com/transportation/crossings/ as of June 2, 2009. New York City's grid pattern and its one-way street system usually provide a good foundation for efficient traffic operations. However, the amount of activity and competition for road capacity and curb space has created inefficiencies for truck movements throughout the City. 2 2 U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau, New York County Quickfacts (Washington, DC: 2008), available at http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/36/36061.html as of June 3. |
|
United States Department of Transportation - Federal Highway Administration |
||