2019 Road Weather Management Performance Measures UpdateChapter 5. Partnerships and Stakeholder CollaborationOverviewThrough partnerships and stakeholder collaboration, the Road Weather Management Program (RWMP) utilizes a multidisciplinary approach to address road weather challenges. By partnering with State departments of transportation (DOT) on research projects and attending and presenting at conferences, workshops, or meetings, the RWMP strives to build partnerships that will advance road weather innovations and practices. RWMP promotes data sharing and information exchange opportunities in order to create a collaborative and comprehensive road weather program. This chapter highlights the extent that the RWMP is fostering and encouraging effective partnerhsips and stakeholder collaboration. Performance FindingsParticipation in Road Weather Program Research and Development ActivitiesInformation sharing and collaboration are fundamental to road weather management. The RWMP facilitates these by partnering with State and local transportation agencies to advance various research and development (R&D) projects. Figure 19 shows three of these projects: the Pathfinder Initiative, Integrated Mobile Observations (IMO) program, and Road Weather Management Capability Maturity Framework (RWM CMF). All three projects have shown continued growth since the 2015 update, indicating the success of the RWMP's outreach and collaboration efforts. 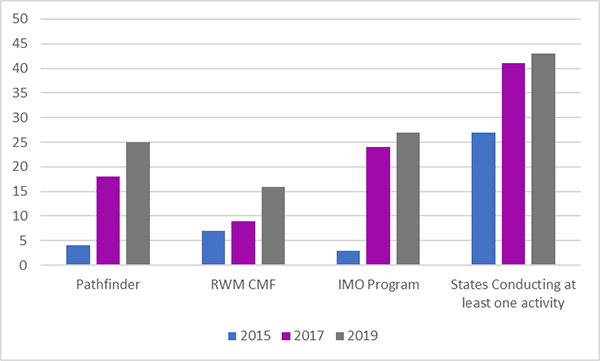 The x-axis displays the four clusters of the categories Pathfinder RWM CMF, IMO Program, and States Conducting at least one activity. Each cluster contains the three bars with a line for 2015, a line for 2017, and a line for 2019. The y-axis ranks the agencies from zero to 50 and increases in increments of five. Most states were conducting at least one activity, but other programs had lower participation rates.
The x-axis displays the four clusters of the categories Pathfinder RWM CMF, IMO Program, and States Conducting at least one activity. Each cluster contains the three bars with a line for 2015, a line for 2017, and a line for 2019. The y-axis ranks the agencies from zero to 50 and increases in increments of five. Most states were conducting at least one activity, but other programs had lower participation rates.Figure 19. Graph. Number of agencies participating in road weather research and development projects. Participation in Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest SystemThe RWMP supports the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) by working with State DOTs to sign data-sharing agreements and ensure data quality by integrating quality checking algorithms into the system. Since 2017, the number of respondents to the State DOT survey indicating their agency subscribed to NOAA's Meteorological Assimilation Data Ingest System (MADIS) dropped from 21 to 13. One reason could be that the MADIS system has still not deployed the QA/QC algorithms that were specifically identified by the DOTs. As NOAA development of MADIS continues, the usage by State DOTs may increase once the QA/QC requirements of the DOTs are available in production. Engagement with the National Weather ServiceLocal weather forecast information is a critical input in road weather management and operations decision-making. The RWMP also supports the National Weather Service (NWS) by encouraging State DOTs to use tools such as NWSchat, which gives DOTs access to real-time weather forecasts. The RWMP tracks the number of agencies that coordinate with their local forecast offices for assistance in road weather management and operations (see Figure 20). Every respondent (100%) indicated that their agency worked with their local forecast offices, with over 70% indicating routine coordination during inclement weather events. As part of Pathfinder, engagement with the NWS also includes greater coordination with the private sector weather providers. 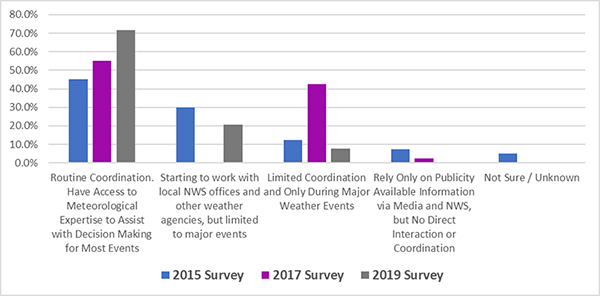 The x-axis shows the level of coordination occurring in the five categories of Routine Coordination, Have Access to Meteorological Expertise to Assist with Decision Making for Most Events, Starting to Work with Local NWS Offices and Other Agencies, but limited to Major Events, Limited Coordination and Only During Major Weather Events, Rely on Publicly Available Information via media, but no direct Action or Coordination, and Not Sure/Unknown. The y-axis ranks the coordination from 0% to 80% in increments of 10%. Each cluster contains the three bars with a line for 2015, a line for 2017, and a line for 2019. Over a four-year period from 2015-2019, most states had routine coordination.
The x-axis shows the level of coordination occurring in the five categories of Routine Coordination, Have Access to Meteorological Expertise to Assist with Decision Making for Most Events, Starting to Work with Local NWS Offices and Other Agencies, but limited to Major Events, Limited Coordination and Only During Major Weather Events, Rely on Publicly Available Information via media, but no direct Action or Coordination, and Not Sure/Unknown. The y-axis ranks the coordination from 0% to 80% in increments of 10%. Each cluster contains the three bars with a line for 2015, a line for 2017, and a line for 2019. Over a four-year period from 2015-2019, most states had routine coordination.Figure 20. Graph. Level of coordination between State DOTs and NWS local forecast offices. |
|
United States Department of Transportation - Federal Highway Administration |
||