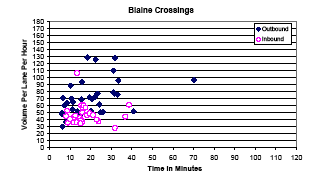
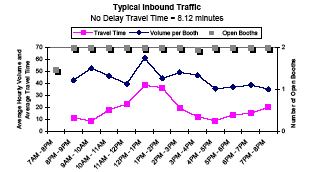
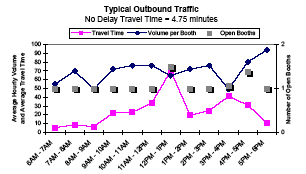
Blaine Crossing Summary
The Pacific Highway (Blaine Border) Crossing is the major truck border crossing linking western Washington state with the coastal mainland of British Columbia (BC). The border between Washington and BC is located on the 49th parallel and since it is defined by degrees of latitude north of the equator it does not correspond to any natural feature such as a river. Consequently, there is only an imaginary line demarcating the border and no bridge or toll facility. The border crossing is the mandatory crossing point for all trucks traveling north on I-5 towards BC and south on BC route 99 towards Washington State.
The Blaine crossing is located about one mile to the east of the auto crossing. The Blaine Border Crossing is the gateway that trucks traveling from Seattle north to Vancouver or Vancouver south to Seattle and beyond use. Trucks traveling north on I-5 must exit the Interstate at state route 543, cross the border about a mile to the north then continue north on BC route 15 to BC route 914. On BC route 914, the trucks travel west to join the BC route 99, the major route north to Vancouver. Heading south the process is reversed.
| Baseline Time[1] | Average Crossing Time[2] | 95th Percentile Time[3] | Buffer Time[4] | Buffer Index[5] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outbound | 4.8 | 21.0 |
9.1 | 14.3 | 66.5 |
| Inbound | 8.1 | 17.3 | 80.3 | 18.3 | 105.8 |
Notes:
- Baseline time (in minutes) to travel the study distance (between the starting point in the exporting country and the initial inspection point in the importing country) in free-flow traffic conditions.
- Average crossing time (in minutes) to travel the study distance.
- Time (in minutes) for 95 percent of trucks to travel the study distance.
- Time (in minutes) between the average time and the 95th percentile time for trucks to travel the study distance. This is the "extra time" that must be budgeted to cross the border relative to the average time.
- Buffer time necessary expressed as a percentage of average time. This is the extra percentage of average time that must be budgeted to cross the border.