Work Zone ITS Overview Webinar January 30, 2014
Overview of Work Zone ITS and New FHWA Resources
slide 1
Overview of Work Zone ITS and New FHWA Resources

U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
Tracy Scriba, FHWA
January 2014
slide notes:
None
slide 2
Presentation Outline
|
 |
slide notes:
None
slide 3
What is Work Zone ITS?
- Use of communications-based information and electronics technologies
- In and around work zones
- To improve/maintain safety, mobility, and/or customer satisfaction
- With portable and temporary components in most cases, that may be combined with permanent ITS
- May be leased or purchased or acquired indirectly
| WZ ITS = using technology to support effective work zone management and operations |
slide notes:
WZ ITS is used to improve/maintain safety, mobility, or customer satisfaction, It may have a primary focus on one of these, but it often supports all 3 and may also help contractor prodctivity.
Smart work zones are usually Portable and Temporary, lasting last the duration of the road improvement project and then being moved to other road project work zones over time or returned to the vendor.
However, in some situations the systems can be Fixed, for example when part or all of a multi-year work zone ITS deployment is left in place and incorporated into permanent traffic monitoring and management systems.
slide 4
WZ ITS Components
- Sensors that collect data on traffic conditions
- Communications equipment to transmit the data
- Software to process/analyze the data and data storage
- Electronic equipment to:
- Disseminate information to end users
- Implement traffic control/management decisions
slide notes:
None
slide 5
History
- Handful of companies, each with one to a few products
- Products tended to be systems → Not very flexible
- Each deployment an adventure/experiment
- Lots of learning
- Not enough thought into systems
- As many failures as successes
slide notes:
None
slide 6
WZ ITS Has Evolved
- Broader range of products and technologies
- More scalable and flexible
- Better planned (usually)
- More applications
- Leveraging of permanent ITS
- Sometimes accomplished by purchasing data
- Less adventure
- More successes
slide notes:
None
slide 7
Why Consider Using WZ ITS Now?
|
 |
slide notes:
In conclusion...
Photo credit: MnDOT
slide 8
WZ Challenges and ITS
➔ Congestion
- End-of-queue crashes
- Delay
- Dissatisfied motorists (private & commercial)
- Difficulty in emergency vehicle access and response
- Delayed contractor vehicle access (reduced efficiency)
✓ Speed detection and warning systems
✓ Traveler information systems, active diversion
✓ Data on best times to work and for deliveries
slide notes:
None
slide 9
WZ Challenges and ITS
➔ Speeding/Speed Management
- Setting speed limits
- Compliance with speed limits
- Limited areas for law enforcement officer stationing
- Limited areas to pullover speeders
✓ Speed monitoring systems
✓ Variable speed limit systems
✓ Automated enforcement systems
slide notes:
None
slide 10
WZ Challenges and ITS
➔ Crashes
- Timeliness of incident detection and response
- Congestion
- Secondary crashes
- Intrusions
- Work vehicle access/egress
✓ Cameras and queue detection systems
✓ Intrusion alarms
✓ Signs warning of entering/leaving roadway
slide notes:
None
slide 11
WZ Challenges and ITS
➔ Performance Monitoring
- Lack of data
- Limited personnel to gather data
- Difficulty in assessing impacts/estimating performance
- Unknowns about appropriate work windows
- Unknown effectiveness of WZ strategies
✓ Systems gather lots of data automatically (archiving)
✓ Exposure/volumes, travel speeds (delays, queues) can help assess impacts on conditions
✓ Determine best times to work
✓ Document effects of different WZ strategies
slide notes:
None
slide 12
Benefits Found in Using WZ ITS
A study of successful deployments showed that:
- 50-85% of drivers surveyed said they changed their route in response to WZ ITS info
- Queue length reductions up to 56-60% are possible
- Speed monitoring displays reduced speeds by 4-6 mph
- One study found a 20-40% reduction in vehicles traveling ≥ 10 mph over the speed limit when SMDs were used
slide notes:
Queue length – example results:
For example, Minnesota DOT evaluated dynamic late merge and found the system:
- Shortened queue length by 35%
- Equalized use of lanes and speeds between lanes
- Eliminated confusion over lane use and correct merge point
- Reduced aggressive driving
- Did not change throughput
- Improved mobility and traffic management
- More informed public
- Greater safety of workers and travelers
- Reduced crashes
- Quicker incident response
- Better PR and relationships with stakeholders
- Enhanced speed management
- Better understanding of traffic conditions
- Enhanced contract management
slide 13
ITS Applications in Work Zones
|
 |
slide notes:
Michigan VSL deployment
Photo taken by Tracy Scriba
slide 14
Traffic Monitoring and Management
Dynamic Lane Merge Systems:
- Monitor traffic and regulate merging approaching lane closures
- Intended to smooth traffic flow and improve safety by increasing consistency in merge behavior
- Can be used to encourage early merge or late merge
| Has been used in a few States, including MI and MN |
slide notes:
The system monitors traffic conditions ands encourages condition responsive merging.
Early merge: When traffic volumes are lower, the system encourages early merging
Late merge: During congestion, encourages use of both lanes to merge point to limit queue length and maximize the use of lanes for storage
A system can be used for one or both types of merges
slide 15
Traveler Information
- Sensors to monitor real-time traffic conditions
- Data used to calculate delay/speed/travel time
- Info automatically displayed on CMS, website (map, CMS messages), HAR
- Cameras to gather additional condition info
| Has been used in many States |
slide notes:
None
slide 16
ITS for Traffic Mgmt/Route Choice
- Provide travel times along arterial and Interstate
- Enable route choice
Sequencing Travel Time Sign on State Street Northbound

| Has been used in several States in various forms, including UT |
slide notes:
System used Utah
Photos taken by Tracy Scriba
slide 17
ITS to Mitigate End-of-Queue Crashes
| 
|
| Used in several States, including IL and TX |
slide notes:
System used in Illinois to mitigate end of queue crashes
Photo taken by Tracy Scriba
slide 18
Automated/Technology Assisted Enforcement
| 
|
slide notes:
Photos taken by Tracy Scriba
slide 19
Performance Monitoring/Management
- Slightly historical Inrix Data
- Identify mobility issues, investigate in the field, make changes to address or to notify drivers
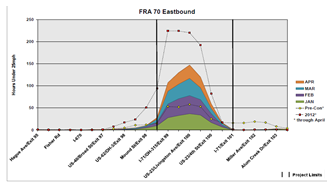
| Has been used in a few States, including OH |
slide notes:
Image: Ohio DOT
slide 20
FHWA ITS in WZ Efforts
- Implementation Guide
- Case Studies
- Peer Exchange
- WZ ITS Leaflet
- Assessment of Effectiveness
- Cross-cutting study
- Connected vehicle research on delivering WZ Info to vehicles
www.ops.fhwa.dot.gov/wz/its/index.htm
slide notes:
Implementation Guide
Help practitioners effectively use WZ ITS as one of many tools for WZ management
- Assessing the Need for WZ ITS
- Detailed System Planning and Design
- Procurement
- System Deployment
- System Operation and Maintenance
- Evaluation
Case Studies
Show how ITS can be used to address WZ safety and mobility issues
- Mitigating End-of-Queue Crashes: Illinois
- Enhancing Route Choice During Construction: Utah
- Permanent ITS to Manage WZ Traffic: Las Vegas
- Performance Specification Monitoring: Utah
slide 21
WZ ITS Case Studies
- Objectives:
- Show how ITS can be used to address WZ safety and mobility issues
- Provide examples of decision-making processes and steps followed by agency/contractor
- Use traditional engineering design process as a roadmap to describe each implementation
- Provide examples for Implementation Guide
slide notes:
None
slide 22
Case Studies
- Mitigating High-Speed End-of-Queue WZ Crashes: Illinois DOT Experiences
- Managing Traffic and Enhancing Route Choice During Construction: Utah DOT I-15 CORE Project
- Traffic Mobility Performance Specification Monitoring: Utah DOT Bangerter Highway Project
- Permanent ITS to Manage WZ Traffic: Las Vegas Transportation Management Center
slide notes:
None
slide 23
Case Study Organization
| 
|
slide notes:
None
slide 24
WZ ITS Implementation Guide
- Objective: Help practitioners effectively use WZ ITS as one of many tools available for WZ safety and mobility management
- Content:
- Focuses on process
- Provides considerations from needs assessment through evaluation
- Comes from 5 case studies done for this project, 2013 peer exchange, and prior research (evaluations, case studies, etc.)
slide notes:
None
slide 25
WZ ITS Implementation Guide
A few key points:
- Does not prescribe warrants for use, but provides examples of ways to decide on use
- WZ ITS is one strategy in the toolbox
- Need a combination of strategies
- Strategies should be chosen to solve specific problems
- All strategies – including ITS – should not be considered independently
- Use the impacts assessment and TMP development process to identify issues and select strategies
- Better planning increases the likelihood of successful deployment
slide notes:
WZ management strategies include:
- Project Coordination and Scheduling
- Contracting
- Construction Methods
- Transportation Management
- Public Information
ITS is one of many possible ways to address the issues identified for a particular work zone.